Choosing the right construction method can make or break your industrial or commercial project. Two major building systems dominate the market: PEB (Pre-Engineered Buildings) and RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) buildings.
While RCC has been the traditional choice, PEB structures are gaining popularity because of faster construction, cost savings, flexibility, and durability.
This guide will explain the key differences between PEB and RCC, helping businesses, industries, and contractors make an informed decision.
Target keywords: PEB buildings, RCC buildings, pre-engineered building advantages, industrial steel structures, cost-effective warehouses
What is a PEB Building?
A PEB (Pre Engineering Building) is a steel structure that is designed, fabricated, and manufactured in a factory. All components primary frames, secondary members, roof panels, wall cladding, and accessories are prefabricated and shipped to the site for assembly.
Benefits of PEB Buildings:
- Faster construction and installation
- Cost-effective solution for industrial projects
- High tensile strength and durability
- Lightweight steel reduces foundation costs
- Modular design allows easy expansion
- Eco-friendly and recyclable.
Common Uses of PEB:
- Warehouses & logistics centres
- Factories & manufacturing units
- Cold storage & food processing
- Workshops & industrial sheds
- Utility buildings & water treatment facilities
What is an RCC Building?
RCC buildings are those that are constructed at the site by mixing concrete with steel reinforcement bars. Concrete provides the compressive strength and steel provides tensile strength.
Advantages of RCC buildings:
- High vertical load-bearing capacity
- Durable for multi-storey construction
- Appropriate for residential apartments and government buildings
- Ideal for heavy civil infrastructure projects
Limitations:
- Slower construction due to curing and multiple on-site processes
- Higher labour and material costs
- Expansion and modifications are difficult
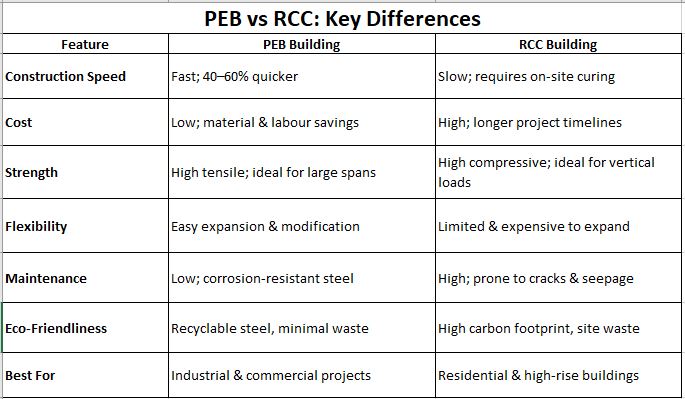
PEB vs RCC: Key Differences
Why Choose PEB for Industrial Projects?
- Faster Construction: Pre-fabrication allows parallel manufacturing and site prep.
- Cost-Effective: Reduced labour, less material wastage, and shorter timelines.
- Durable & Low Maintenance: Coatings like FBE, Epoxy, or Zinc-Aluminium increase lifespan.
- Flexible & Expandable: Modular design supports future growth.
- Eco-Friendly: Minimal site waste and recyclable steel.
Industries Using PEB: Warehousing, manufacturing, logistics, cold storage, agriculture, utilities.
Strength & Durability: PEB vs RCC
- PEB: Lightweight steel frame, resistant to wind, earthquake, and industrial loads.
- RCC: Heavy, strong vertical support; ideal for multi-storey buildings.
Verdict: PEB is ideal for large industrial spans; RCC is better for tall or heavily-loaded structures.
Design & Aesthetics
PEB: Modern industrial look, clean lines, customizable cladding. (Cladding, Purlins & Frames)
RCC: Unlimited design freedom, suitable for high-rise and architectural projects.
Maintenance & Lifespan
PEB: Minimal maintenance, lifespan 50+ years with protective coatings.
RCC: Requires crack repair, waterproofing, and occasional rebar treatment.
PEB vs RCC Buildings - FAQ's
1. What is the main difference between PEB and RCC buildings?
PEB is pre-engineered and assembled on-site, RCC is built entirely on-site using concrete and steel. PEB is faster and cost-effective; RCC is suitable for multi-storey buildings.
2. Which is stronger PEB or RCC?
PEB has high tensile strength, suitable for industrial loads. RCC has high compressive strength, ideal for vertical-heavy structures.
3. Why is PEB faster to construct?
PEB components are factory-made and shipped for assembly. No on-site curing or shuttering delays reduce construction time by 40–60%. (PEB vs Conventional Building)
4. Is PEB more cost-effective than RCC?
Yes, due to lower labour, minimal waste, faster project completion, and lower maintenance.
5. How durable are PEB buildings?
With proper coatings, PEB buildings last 50+ years and resist corrosion, wind, and industrial wear.
6. Can PEB buildings be expanded?
Yes, modular design allows easy addition of bays or sections. RCC expansion is costly and complex.
7. Are PEB buildings suitable for harsh weather?
Yes, engineered for wind, seismic, snow loads, and coastal climates. Protective coatings enhance durability.
8. What maintenance does a PEB building require?
Minimal regular inspections and occasional cleaning are sufficient. Coatings prevent rusting.
9. Which industries prefer PEB buildings?
Warehousing, manufacturing, logistics, cold storage, agriculture, and utilities prefer PEB for speed, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
Why Partner with Rostfrei Steels for PEB Structures?
Rostfrei Steels offers:
- Custom PEB engineering & design
- Factory-fabricated international-grade steel structures
- Corrosion-resistant coatings
- Quick on-site installation
Combined PEB + storage tank solutions




